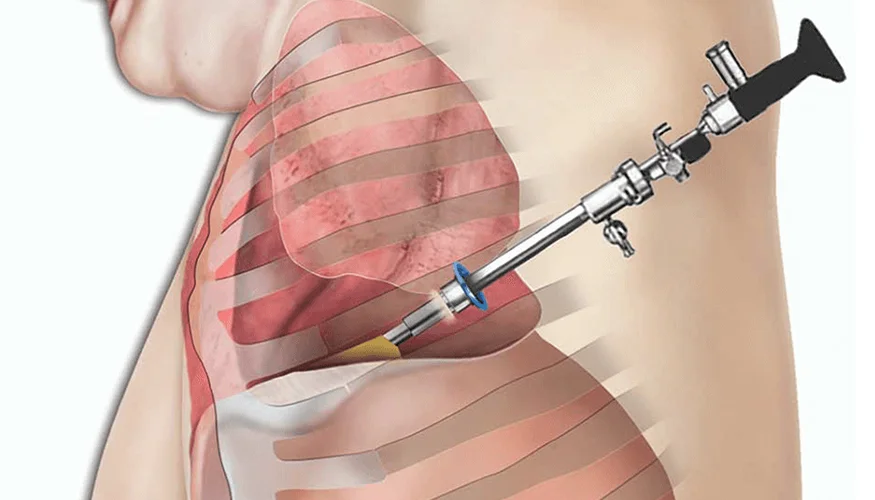
What is Thoracoscopy?
Thoracoscopy, also known as pleuroscopy, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows doctors to examine the pleural space the area between the lungs and the chest wall. This procedure is used to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the pleura, lungs, and other structures within the chest cavity.
Why Do You Need Thoracoscopy?
Thoracoscopy is a medical procedure performed for several reasons, including diagnosing and treating lung and chest conditions. Here are the primary reasons you might need thoracoscopy:
Diagnosing Lung Problems
Thoracoscopy is often used to determine the cause of various lung issues, such as difficulty breathing or coughing up blood. It allows doctors to visually inspect the lungs and surrounding areas to identify abnormalities or diseases.
Investigating Suspicious Chest Areas
If imaging tests like a chest X-ray or CT scan reveal abnormal areas, thoracoscopy can be utilized to examine these areas more closely. It also allows for the collection of biopsy samples from lymph nodes, abnormal lung tissue, the chest wall, or the pleura (lining of the lung). This procedure is particularly useful for diagnosing conditions like mesothelioma and lung cancer.
Treating Small Lung Cancers
In some cases, thoracoscopy can be employed to treat small lung cancers by surgically removing the tumor. This may involve a wedge resection (removing the part of the lung with the tumor) or a lobectomy (removing a lobe of the lung if the tumor is larger). Thoracoscopy may also be used to treat cancers of the esophagus or thymus gland.
Managing Fluid Around the Lungs
Thoracoscopy can be performed to remove excess fluid from around the lungs, which can alleviate breathing difficulties. The fluid collected can be analyzed in a lab to check for cancer or infections. If the fluid tends to accumulate again, thoracoscopy can be used to administer medication into the chest cavity to prevent further buildup, a procedure known as pleurodesis.
Thoracoscopy is a versatile procedure that provides both diagnostic and therapeutic benefits, helping to address and manage various lung and chest conditions effectively.
Benefits of Thoracoscopy
- Minimally Invasive: Compared to open chest surgery, thoracoscopy involves smaller incisions, leading to less pain and faster recovery.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Provides direct visualization and access to the pleural space for accurate diagnosis and targeted biopsies.
- Effective Treatment: Enables various therapeutic interventions, such as fluid drainage and pleurodesis, improving patient outcomes.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Due to its minimally invasive nature, patients often experience shorter hospital stays and quicker return to normal activities.
Contact Us
For more information or to schedule a consultation for thoracoscopy, contact Pulmonologist Dr. Rushi Desai today. Our team provides the highest standard of care for your respiratory health.
Need a help ?
Best Treatments
Our Best Treatments
Asthma and Allergy Tests are diagnostic procedures used to identify specific allergens that trigger asthma or allergic reactions. These tests help in understanding the causes of respiratory issues and allergic symptoms, enabling precise treatment and management.
- Asthma Tests: Include lung function tests like spirometry, which measure the amount and speed of air a person can inhale and exhale, helping to diagnose and monitor asthma severity.
- Allergy Tests: Commonly involve skin prick tests or blood tests (such as ImmunoCAP) to detect allergic sensitivities to various substances like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain foods.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation due to airway and/or alveolar abnormalities. It includes conditions such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Early detection and management are crucial in slowing the progression of COPD and reducing the risk of complications.
Read More about COPDLung Cancer is a serious disease where abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the lungs, forming tumors. The main types are non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Common symptoms include persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood. Lung cancer is detected through imaging tests such as X-rays and CT scans and confirmed with a biopsy. Early detection significantly improves treatment success and survival rates.
Read More about Lung CancerInterstitial Lung Disease (ILD) is a group of disorders characterized by progressive scarring (fibrosis) of the lung tissue, which affects the interstitium the network of tissue that supports the lungs' air sacs (alveoli). This scarring makes it difficult for the lungs to expand and contract properly, leading to breathing difficulties and reduced oxygen supply to the bloodstream.
Read More about Interstitial Lung disease
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs but can also impact other parts of the body such as the kidneys, spine, and brain. TB spreads through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. TB is treatable and curable with a strict regimen of antibiotics taken over several months. Early detection and adherence to the prescribed treatment are essential to prevent the spread of the disease and to achieve a full recovery.
Read More about TuberculosisSleep Apnoea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These interruptions, called apnoeas, can last from a few seconds to a minute and can occur numerous times throughout the night. The most common type is obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), which occurs when the throat muscles relax and block the airway. Central sleep apnoea (CSA), a less common form, happens when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Read More about Sleep Apnoea
Occupational Lung Diseases are respiratory conditions caused by exposure to harmful substances in the workplace. These diseases can result from inhaling dust, chemicals, fumes, or other hazardous materials over an extended period.
Read More about Occupational Lung DiseasesPleural Effusion is a condition where excess fluid accumulates in the pleural space, the thin cavity between the lungs and the chest wall. This fluid buildup can compress the lungs, making it difficult to breathe and causing chest pain.
Read More about Pleural DiseasesRigid Bronchoscopy is a medical procedure used to examine and treat problems in the airways (bronchi) and lungs using a rigid, hollow tube called a bronchoscope. Unlike flexible bronchoscopy, which uses a flexible tube, rigid bronchoscopy allows for larger instruments to be passed through the tube, facilitating interventions.
Read More about BronchoscopyEBUS (Endobronchial Ultrasound) refers to two types: Linear and Radial EBUS, both of which are advanced bronchoscopic techniques used for detailed imaging and biopsy of structures near the lungs. Both types of EBUS are minimally invasive procedures performed under sedation or general anesthesia by pulmonologists or interventional bronchoscopists.
Read More about EBUS (Linear & Radial)
Rigid Thoracoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to examine and treat conditions affecting the chest cavity, specifically the pleural space (the area between the lungs and the chest wall). It involves the use of a rigid thoracoscope, a tubular instrument with a camera and light source at its tip, which is inserted through a small incision made in the chest wall.
Read More about ThoracoscopyPediatric Bronchoscopy is a medical procedure used to examine and treat the airways (bronchi and bronchioles) in children. It involves inserting a flexible or rigid bronchoscope through the nose or mouth and into the airways, allowing direct visualization and access to the lungs.
Read More about EBUS (Linear & Radial)
Tracheal Stenting is a medical procedure used to treat narrowing or obstruction of the trachea (windpipe) by inserting a stent—a small, flexible tube—into the affected area to keep it open. This procedure is typically performed in cases where there is significant narrowing of the trachea due to conditions such as: Tumors, Trauma, Inflammatory Conditions, and Congenital Anomalies.
Read More about Tracheal Stenting
Lung Transplantation is a surgical procedure performed to replace one or both diseased lungs with healthy lungs from a deceased donor. This complex procedure is typically considered for patients with end-stage lung disease that cannot be adequately treated with other medical or surgical interventions.
Read More about Lung TransplantsTracheal Stenosis Repair is a surgical procedure aimed at correcting narrowing or constriction of the trachea (windpipe), which can restrict airflow and lead to breathing difficulties.
Read More about Tracheal stenosis repair
Endobronchial Tumour Debulking is a procedure performed to remove or reduce the size of tumors located within the bronchial airways using various techniques and tools. This approach is often used to relieve symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath caused by obstructive tumors.
Read More about Endobronchial tumour debulking
Lung Cryo Biopsies (or Cryo Lung Biopsies) are minimally invasive procedures used to obtain tissue samples from the lungs for diagnostic purposes. This technique involves using extreme cold to freeze and then remove a small piece of lung tissue, which is then examined under a microscope to identify and diagnose lung conditions such as interstitial lung diseases, lung infections, and lung cancers.
Read More about Lung Cryo biopsiesAblation of Lung Cancer Lesions refers to the targeted destruction or removal of cancerous lesions in the lungs using various minimally invasive techniques. These procedures are typically performed when surgery is not an option or as part of a comprehensive treatment plan to manage lung cancer.
Read More about Ablation of lung cancer lesionsBalloon Dilatation is a medical procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed passages within the body, such as blood vessels or airways, using an inflatable balloon. In the context of respiratory medicine, balloon dilatation is commonly performed to alleviate narrowing in the airways (bronchi) caused by conditions such as: Tracheal Stenosis and Bronchial Stenosis.
Read More about Balloon Dilatation
Aspirated Foreign Body Removal is a medical procedure performed to extract objects or substances that have been accidentally inhaled into the airways (trachea, bronchi) or lungs. This commonly occurs in children but can also affect adults, leading to respiratory distress and potentially life-threatening complications if not promptly addressed.
Read More about Aspirated foreignbody removal
Bronchial Thermoplasty is an innovative procedure used to treat severe asthma by targeting the smooth muscle lining the airways (bronchi). This procedure aims to reduce the excessive smooth muscle that contributes to airway constriction in asthma patients, thereby improving asthma control and reducing symptoms.
Read More about Bronchial ThermoplastyPulmonary Function Testing (PFT) refers to a group of non-invasive tests that assess how well the lungs are functioning. These tests measure various aspects of lung capacity, airflow, and gas exchange to help diagnose respiratory conditions, monitor lung diseases, and evaluate lung function before surgery or as part of occupational health assessments.
Read More about Pulmonary Function TestA Sleep Study, also known as polysomnography (PSG), is a diagnostic test used to evaluate sleep patterns and diagnose sleep disorders. It involves monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep to assess factors such as breathing patterns, brain activity, heart rate, and body movements.
Read More about Sleep DisordersAn Allergy Skin Test is a diagnostic procedure used to identify specific allergens that may be triggering allergic reactions in an individual. It is a common method used by allergists and immunologists to diagnose allergies such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever), asthma, eczema, food allergies, and allergic reactions to medications or insect stings.
Read More about Allergy Skin TestThe Respiratory Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is a specialized medical unit within a hospital that provides intensive care and monitoring for patients with severe respiratory illnesses and conditions. It is staffed by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals trained in critical care and respiratory medicine, including pulmonologists, intensivists, respiratory therapists, nurses, and support staff.
Read More about Respiratory ICU

